Check in regularly for information on upcoming updates, outages or IT news.
I hope this message finds you well. Enthusiasm about artificial intelligence (AI) tools are at an all-time high in academic campuses across the country. Recent advances in AI technologies have made accessibility to these tools easier than ever, raising concerns for some and excitement for others.
We are excited to kick off a three-part series, “AI is here. Now what?” This series is aimed at demystifying the role of Artificial Intelligence in research and healthcare. This first installment will focus on the benefits that AI brings to our field, with a special emphasis on Generative AI.
A Brief History of AI
While the term ‘artificial intelligence’ was not coined until 1956, the concept of “thinking machines” has been around since the ENIGMA code was broken in 1941. Fast forward to 2014, a new dawn of AI was born: Generative AI. This technology can generate text, images and other media in response to prompts. The new generation of Generative AI offerings - ChatGPT, Scribe, Jasper, DALL-E 2 and Bard - utilize Natural Language Processing to generate coherent and contextually relevant text, create digital images and even develop computer programming code.
Why the Hype Now?
Generative AI has been around since 2014, but it has recently gained significant attention. Why? Because it has become more accessible, user-friendly and cost-effective. The average person can now interact with AI in a conversational manner and witness human-like responses thanks to advancements and the availability of free Generative AI apps. These articles from Reuters and McKinsey & Company explain how ChatGPT and other Generative AI models have changed how we view AI.
Benefits of AI in Research and Healthcare
Research Assistance: Generative AI, with its ability to process vast amounts of data quickly, significantly enhances research efforts. It aids in data collection and analysis, potentially uncovering current trends, correlations or insights that might have otherwise been overlooked through traditional research methods. This can lead to more comprehensive and accurate findings to accelerate the pace of scientific discovery.
Information Organization: In the realm of data management, Generative AI plays a pivotal role. It can efficiently organize and categorize vast datasets, simplifying data retrieval and management processes. By automating this task, researchers and healthcare professionals can focus more on the analysis and interpretation of data.
Data Visualization: Generative AI tools can transform complex data into visually intuitive representations, such as diagrams, interactive charts and infographics. These visualizations not only simplify data comprehension, but also facilitate effective communication of research findings and insights within multidisciplinary teams. They bridge the gap between data analysts and non-technical stakeholders, ensuring a more holistic understanding of the data's significance.
Improved Diagnostics: One of the most transformative applications of AI in healthcare is its role in diagnostics. AI algorithms can analyze medical images such as X-rays, MRIs and CT scans, as well as pathology slides and genetic sequences, with remarkable accuracy. This has the potential to expedite diagnosis and reduce the likelihood of errors, improving patient outcomes.
Data Analytics and Insights: AI excels in handling and analyzing large, complex datasets. It can sift through vast volumes of data to identify intricate patterns, trends or anomalies that might be imperceptible to human researchers. These insights are invaluable for both research endeavors and the development of personalized treatment plans in healthcare. AI-driven analytics enable data-driven decision-making which can lead to more effective and targeted interventions.
Want to learn more about how generative AI is being developed and used?
Check out these articles by IBM, Data Science UA and HealthTech on the benefits of AI in healthcare and research.
From accelerating research progress to enhancing data management, simplifying data visualization and revolutionizing diagnostics and data analytics, AI is a powerful tool. It holds the potential to revolutionize healthcare fields. Understanding the benefits of AI, particularly Generative AI, can help us harness its potential to improve patient outcomes and streamline research processes. Stay tuned for Part 2 of this series, where we will delve into the risks and ethical considerations of using AI in Healthcare and Research Fields.
Thank you for joining us on this exploration of Generative AI's potential.
Welcome to Part 2 of our series, "AI is here. Now What?" In the first installment, we explored the exciting benefits of AI, focusing on Generative AI. In Part 2, let’s explore the complex terrain of AI ethics and the potential pitfalls as we continue our journey through the world of artificial intelligence in healthcare and research.
AI: The Dark Side
To harness the potential of AI to improve patient outcomes and streamline research processes, it's crucial to understand the challenges and ethical dilemmas that come with this powerful technology. Below, we have compiled a few of the key challenges of Generative AI in healthcare and research.
Challenges and Risks in AI
Data Purity: One of the most significant challenges with AI lies in the limited understanding that organizations possess regarding the data that underpins AI systems, including lack of insight into how AI is trained and its behavior in various contexts. This knowledge gap poses a substantial risk by eroding trust and causing uncertainty. Moreover, it creates difficulties in validating AI-generated responses.
The issue of data purity becomes even more pronounced when considering AI hallucinations, where large language models like GPT-4 or Google PaLM confidently generate false information. In navigating these complexities, users are confronted with the task of distinguishing between accurate and fabricated content, underscoring the paramount importance of data purity in the realm of AI applications. Check out this article for more information on AI Hallucinations.
Ethical Concerns: AI algorithms, particularly machine learning models, can inherit biases present in the data they are trained on. This bias can lead to unfair or discriminatory decisions. For instance in healthcare, biased algorithms may recommend treatments that favor one demographic over another, which result in inequitable healthcare outcomes. Ethical considerations are essential to ensure AI is used in a fair and just manner.
Data Privacy Concerns: In the realm of healthcare, protecting patient data and compliance with HIPAA is paramount. Generative AI are trained using synthetic datasets; in other words, they are like a child who listens to your every word and then regurgitates those words at will. Remember that AI will take any information you provide and potentially use it when responding to other organization's AI prompts. Confidential (PHI, PII) or restricted (non-public info such as research or financial data) information should never be uploaded or used on any AI application. Please only input data that is accessible to the public.
For further insights into the intersection of Health Care Privacy and artificial intelligence, please explore articles from The Regulatory Review and Bank Info Security. Protecting patient data and adhering to regulatory standards remains a top priority as we navigate the evolving landscape of AI in healthcare and research.
Security Vulnerabilities: AI is not immune to exploitation by threat actors. Cybercriminals are already harnessing AI to create advanced phishing attacks and synthetic media, such as digitally altered video and voice clones for deceiving targeted victims. Even ChatGPT has been utilized in the design of malware and information stealing virus' that can bypass modern security controls. This alarming trend highlights the growing efforts of cybercriminals to weaponize AI tools, making discussions on platforms like ChatGPT one of the hottest topics on the dark web.
What to learn more about the risks of AI?
Check out these articles from Built In and Forbes.
In navigating the "dark side" of AI, it is crucial for us to stay informed, implement robust cybersecurity measures and prioritize ethical considerations. Responsible AI development and usage can mitigate these challenges and ensure the benefits of AI are realized while minimizing the associated risks. Stay tuned for Part 3 of this series, where we will discuss the do’s and don'ts of AI and the steps you need to take to use AI in your work.
Thank you for joining us on this exploration of Generative AI in Healthcare and Research
Welcome back to our three-part series on the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in research and healthcare. Part 1 of our series, "AI is here. Now What?," unveiled the remarkable potential of Artificial Intelligence in healthcare and research. We explored the inception of Generative AI, its evolution and its accessibility to individuals today. The benefits of AI in research and healthcare were elucidated, including its role in data analysis, information organization, data visualization, diagnostics and data analytics.
Part 2 delved into the risks and ethical considerations associated with AI in our field. We discussed challenges such as data purity, ethical concerns stemming from biased algorithms, data privacy compliance and security vulnerabilities. We must navigate these challenges to ensure responsible AI development and usage.
Now, as we embark on Part 3 of our series, we shift our focus to practical guidance. In this segment, we will discuss the do's and don'ts of AI and outline the essential steps you need to take to use AI in your work.
DOs and DON'Ts of AI in Healthcare and Research
As AI continues to shape the landscape of healthcare and research, understanding how to harness its power responsibly and effectively is paramount.
DON'T ignore ethical responsibility: Ethical considerations in AI training data are crucial, as bias can lead to unequal outcomes. It is essential to prioritize fairness and justice in AI utilization to avoid overlooking ethical issues, particularly in domains like healthcare.
DON’T rush to use AI without careful consideration: While AI's data analysis capabilities can uncover hidden patterns and trends, benefiting both research and healthcare, it is important for users to carefully consider how and when to use AI in a safe way.
DON'T enter PII or PHI: Patient and personal privacy should remain our number one priority. Remember that Generative AI will take any information you provide and potentially use this information when responding to other organizations. For this reason, confidential or restricted information should never be uploaded to a Generative AI platform.
DON'T relinquish the human element: While AI can assist with tasks, don't allow it to think on your behalf. AI is devoid of human emotion or thought. Remember the importance of fact-checking and engaging in critical thinking.
DO prioritize cybersecurity: Emphasize cybersecurity to protect against AI-related threats. Cybercriminals use AI for advanced attacks, like deepfakes and polymorphic malware, making vigilance crucial.
DO address data purity: Everyone should understand AI's data foundation and potential biases. This minimizes trust issues and aids in verifying AI-generated responses.
DO ensure data privacy in healthcare: Comply with HIPAA for patient privacy. Use de-identification and synthetic datasets to protect patient information while utilizing AI in healthcare.
DO exercise caution: AI is making many aspects of our work faster, which can make it easier to make mistakes and do bad things. Be concise and careful when leveraging AI tools in the workplace.
How do I get started with Generative AI in my area?
Now that you understand the benefits and challenges of Generative AI like ChatGPT or Bard, you might wonder how your team can leverage this powerful technology.
Good News! You can test drive Generative AI using Copilot, our internally protected chat feature on Bing! Start chatting with a few simple steps!
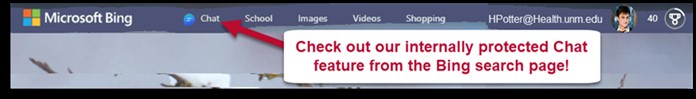
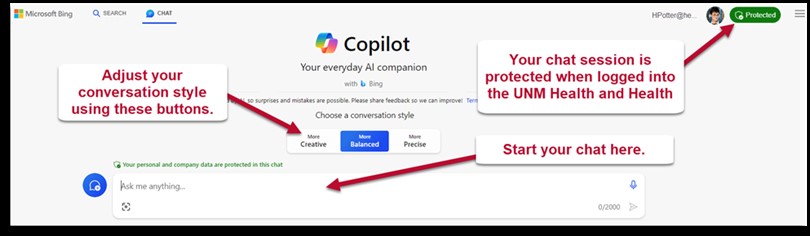
If you choose to utilize AI tools for work other than the internally protected chat described above, there are a couple of things you will need to do.
Want to learn more about AI?
Our three-part series on generative AI only scratched the surface! There is so much more you can learn about how generative AI is transforming research, healthcare and SO much more! Check out this article from HIMSS (Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society) on the power and potential of large language models in healthcare.
Want to test drive AI but don’t know where to start?
Check out this beginner's guide on the basics of writing a prompt to get the best answers. Want to dig deeper? Get more in-depth information about writing effective prompts with this blog from phData.
In Conclusion
Our series has explored AI in healthcare and research. We began by uncovering Generative AI's potential and ethical considerations. Now, in the final part, we offer practical guidance: prioritize cybersecurity, understand data purity and ensure data privacy.
Thank you for joining us on this exploration of AI's potential, challenges and practical applications. We look forward to seeing the positive impact AI will continue to have in healthcare and research as we move forward together.
HSC Chief Information Office
MSC 09 5105
1 University of New Mexico
Albuquerque, NM 87131-0001
Physical Location:
Health Sciences and Service Building
Suite 169
Phone: 505-925-1117
Fax: 505-272-2761
HSC-CIO-Notices@salud.unm.edu